Electromagnetic coils
An electromagnetic coil (or simply a "coil") is formed when a conductor (usually an insulated solid copperwire) is wound around a core or form to create an inductor or electromagnet. One loop of wire is usually referred to as a turn, and a coil consists of one or more turns. For use in an electronic circuit, electrical connection terminals called taps are often connected to a coil. Coils are often coated with varnish and/or wrapped with insulating tape to provide additional insulation and secure them in place. A completed coil assembly with taps is often called a winding. A transformer is an electromagnetic device that has aprimary winding and a secondary winding that transfers energy from one electrical circuit to another byinductive coupling without moving parts. The term tickler coil usually refers to a third coil placed in relation to a primary coil and secondary coil. A coil tap is a wiring feature found on some electrical transformers, inductors and coil pickups, all of which are sets of wire coils. The coil tap(s) are points in a wire coil where a conductive patch has been exposed (usually on a loop of wire that extends out of the main coil body). As self induction is larger for larger coil diameter the current in a thick wire tries to flow on the inside. The ideal use of copper is achieved by foils. Sometimes this means that a spiral is a better alternative. Multilayer coils have the problem of interlayer capacitance, so when multiple layers are needed the shape needs to be radically changed to a short coil with many layers so that the voltage between consecutive layers is smaller (making them more spiral like).
[edit]Analysis
The inductance of single-layer air-cored cylindrical coils can be calculated to a reasonable degree of accuracy with the simplified formula
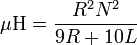
where Henry [µH] (microhenries) are units of inductance, R is the coil radius (measured in inches to the center of the conductor), N is the number of turns, and L is the length of the coil in inches. The online Coil Inductance Calculator calculates the inductance of any coil using this formula. Higher accuracy estimates of coil inductance require calculations of considerably greater complexity.
Note that if the coil has a ferrite core, or one made of another metallic material, its inductance cannot be calculated with this formula.
[edit]Coil examples
Some common electromagnetic coils include:
- A bifilar coil is a coil that employs two parallel windings.
- A Barker coil is used in low field NMR imaging.
- A Balun is set of transformer coils for transmission lines.
- A Braunbeck coil is used in geomagnetic research.
- A degaussing coil is used in the process of removing permanent magnetism (magnetic hysteresis) from an object.
- A choke coil (or choking coil) is low-resistance inductor used to block alternating current while passing direct current.
- A Flat coil is used in thin electric motors.
- A Garrett coil is used in metal detectors.
- A Helmholtz coil is a device for producing a region of nearly uniform magnetic field.
- A hybrid coil (or bridge transformer) is a single transformer that effectively has three windings.
- An induction coil (or ignition coil) is an electrical device in common use as the ignition system (ignition coil or spark coil) of internal-combustion engines.
- A loading coil is, in electronics, a coil (inductor) inserted in a circuit to increase its inductance. Archaically called Pupin coils.
- A multiple coil magnet is an electromagnet that has several coils of wire connected in parallel.
- A Maxwell coil is a device for producing almost a constant magnetic field.
- A Micro coil use in security devices.
- A Oudin coil is a disruptive discharge coil.
- The polyphase coils are connected together in a polyphase system such as a generator or motor.
- A relay coil is the copper winding part of a relay that produces a magnetic field that actuates the mechanism.
- A Repeating coil is a voice-frequency transformer.
- A Rogowski coil is an electrical device for measuring alternating current.
- A Rook coil is a high Q coil wave wound cylindrical coil often used for crystal sets.
- A single coil is a type of pickup for the electric guitar.
- A solenoid is a mechanical device, based on a coil of wire, that usually converts energy into linear motion, however solenoids also come in a rotary motion (normally up to a turn of 90 degrees).
- A Spider coil is a high Q wave wound flat coil often used for crystal sets, that somewhat resembles a spider's web.
- A telephone cord is usually manufactured in a coiled fashion, as to allow maximum length while taking up minimum space when not in use.
- A Tesla coil is category of disruptive discharge coils, usually denoting a resonant transformer that generates very high voltages at radio frequencies.
- A Universal coil or a Dual Lateral coil is a self supporting coil used for high voltage applications.
- A voice coil which is mounted to the moving cone of a loudspeaker.
Other applications of coils exist in the field of electromagnetic devices. A coilgun is a type of cannon that uses a series of electromagnetic coils to accelerate a magnetic shell to very high velocities. The filament of an incandescent light bulb has usually the shape of a coiled coil, in order to fit the long filament in a small space.

No comments:
Post a Comment